Lungs are essential organs responsible for delivering oxygen throughout the body and removing carbon dioxide, a vital process that sustains every cell. Healthy lungs ensure the body functions efficiently, but modern challenges like air pollution, smoking, and respiratory infections can compromise lung function and overall well-being.
In today’s world, maintaining strong and resilient lungs is more important than ever. A sedentary lifestyle and poor air quality contribute to reduced lung capacity and endurance, increasing the risk of chronic conditions. That’s where lung health exercises come in—helping you strengthen respiratory muscles, improve oxygen intake, and enhance lung efficiency.
Simple lung health exercises such as diaphragmatic breathing, pursed-lip breathing, and aerobic activities like walking or swimming can boost your respiratory system. Practicing these regularly can enhance lung performance, reduce breathlessness, and support overall vitality. Incorporating these techniques into your daily routine can be a powerful step toward long-term lung health.
This article explores everything you need to know about lung health exercises, their benefits, how they work, and most importantly, the top 8 lung-strengthening exercises and tips you can incorporate into your daily life.
Why Lung Health Matters
Before starting any routine, it’s important to understand why focusing on lung health is essential. Your lungs play a critical role in keeping your entire body functioning properly.
Oxygen Is Fundamental to Life: Every living cell in the human body depends on a consistent supply of oxygen to function, grow, and repair. Well-functioning, healthy lungs ensure this vital gas is efficiently transported into the bloodstream, allowing your entire system to operate at its best.
Enhanced Immune Defense: Robust lung health contributes significantly to a stronger immune system. By effectively filtering out pathogens and pollutants, healthy lungs serve as a first line of defense, reducing your vulnerability to infections such as the common cold, influenza, bronchitis, and other respiratory illnesses.
Improved Physical Stamina and Performance: Whether you’re engaging in high-intensity sports or performing everyday activities like walking up stairs or carrying groceries, strong and efficient lungs provide your body with the oxygen needed to sustain energy, increase endurance, and reduce fatigue during exertion.
Reduced Rate of Age-Related Decline: As individuals grow older, lung capacity and respiratory strength tend to decline naturally. However, incorporating regular lung health exercises into your lifestyle can significantly slow this deterioration, preserving your breathing efficiency and supporting long-term vitality and independence.
Including lung health exercises into your lifestyle not only strengthens your lungs but also supports your overall well-being. From better energy levels to enhanced immunity, prioritizing your respiratory health is a smart and sustainable choice.
How Lung Exercises Help
Lung health exercises are powerful tools that support better breathing and overall respiratory wellness. They work by increasing lung capacity, allowing your lungs to take in more oxygen and expel more carbon dioxide with each breath. Over time, this helps your body become more efficient at oxygen exchange, which fuels your cells and boosts energy levels.
These exercises also strengthen the respiratory muscles, including the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, making breathing easier and more controlled. By practicing lung health exercises, you help your lungs function at their best, especially important in polluted environments or during seasonal illnesses.
Another major benefit of lung exercises is their ability to clear out stale air, mucus, and toxins from the lungs. This not only promotes cleaner lung tissue but also supports faster recovery for individuals with asthma, COPD, or respiratory infections, including COVID-19.
Finally, lung health exercises promote mental calmness by encouraging slow, deep breathing. This activates the body’s relaxation response, reducing stress and anxiety—making these practices beneficial for both physical and mental health, regardless of age or condition.
Top Lung Health Exercises and Tips
Diaphragmatic Breathing (Belly Breathing)
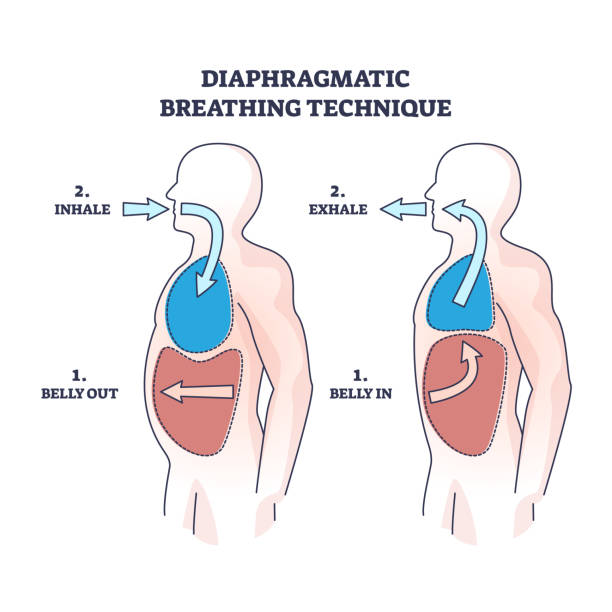
Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as abdominal or belly breathing, is one of the most effective lung health exercises. It targets the diaphragm, the main muscle responsible for deep, efficient breathing. By engaging the diaphragm more actively, this technique helps you draw in more air with less effort.
This exercise involves breathing deeply into your belly rather than shallowly into your chest. As you inhale, your abdomen rises, and as you exhale, it falls. Practicing this regularly improves oxygen intake, reduces shortness of breath, and strengthens respiratory muscles, making it ideal for enhancing lung function.
Diaphragmatic breathing is a simple yet powerful tool for anyone looking to improve respiratory health. Whether you’re managing a lung condition or simply trying to breathe better, incorporating this into your daily routine can support stronger lungs and overall well-being. It’s one of the foundational lung health exercises that benefits people of all ages.
How to Do It
Sit or lie down in a relaxed position.
Place one hand on your chest and the other on your belly.
Inhale deeply through your nose, allowing your belly to rise while keeping your chest still.
Exhale slowly through pursed lips, letting your belly fall.
Repeat for 5–10 minutes daily.
Benefits
Improves oxygen intake.
Reduces breathing effort.
Lowers heart rate and blood pressure.
Encourages full oxygen exchange in the lungs.
Pro Tip: Practice this technique when lying down at first. Once comfortable, try it sitting and then standing.
Pursed-Lip Breathing
Pursed-lip breathing is a simple and effective technique that helps slow your breathing rate and improves air exchange in the lungs. It’s especially useful during physical activity or times of shortness of breath, making it one of the most beneficial lung health exercises.
This method involves inhaling slowly through the nose and exhaling gently through pursed lips, as if you’re blowing out a candle. This controlled breathing keeps airways open longer, allowing more stale air to exit the lungs and making room for fresh oxygen.
Pursed-lip breathing is easy to practice and can be done anywhere. It promotes relaxation, reduces breathlessness, and enhances overall lung efficiency. As part of a regular routine of lung health exercises, it’s especially helpful for individuals with COPD, asthma, or those recovering from respiratory illnesses. It’s also a great tool for anyone seeking better breath control and lung strength.
How to Do It
Inhale through your nose for 2 seconds.
Purse your lips as if you are about to whistle.
Exhale slowly through pursed lips for 4–6 seconds.
Repeat for several minutes.
Benefits
Keeps airways open longer.
Reduces shortness of breath.
Helps eliminate trapped air in the lungs.
Ideal For: People with asthma, COPD, or breathlessness during exercise.
Rib Stretching Exercises

Chest expansion stretches are targeted movements designed to open up the rib cage and enhance lung capacity. By creating more space in the chest cavity, these stretches allow the lungs to expand more fully during each breath, making them valuable lung health exercises.
These stretches often involve raising the arms, interlacing the fingers behind the back, or arching the chest forward while inhaling deeply. The goal is to loosen tight chest muscles and improve posture, both of which contribute to better lung function and easier breathing.
Regular practice of chest expansion stretches can greatly benefit those with restricted breathing due to poor posture, sedentary habits, or respiratory conditions. When included in a daily routine of lung health exercises, they help increase flexibility, support deeper breathing, and improve overall respiratory efficiency. They’re simple, gentle, and effective for people of all fitness levels.
How to Do It
Stand upright and exhale completely.
Inhale slowly, filling your lungs as much as possible.
Hold your breath for 10–15 seconds.
Slowly exhale.
Repeat 3–5 times.
Benefits
Increases flexibility of the thoracic region.
Enhances lung capacity.
Improves posture and reduces shallow breathing.
Pro Tip: Include these into your morning routine or post-exercise cool-down.
Breath-Holding Exercises (Box Breathing)
Box breathing, also known as controlled breath-holding, is a powerful technique used to enhance lung capacity, improve focus, and reduce stress. This method involves breathing in, holding the breath, exhaling, and holding again—each for equal counts, usually four seconds. It’s one of the most calming and effective lung health exercises.
The practice strengthens your respiratory muscles and increases your lungs’ ability to hold air, making breathing more efficient over time. It also slows the breathing rate, helping to regulate oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange, which is essential for maintaining healthy lung function.
Box breathing is not only a great tool for lung support but also for mental clarity and emotional control. Athletes, military personnel, and people recovering from respiratory illness often use it as part of their lung health exercises routine. It’s simple, requires no equipment, and can be practiced anywhere for lasting benefits.
How to Do It
Inhale for 4 seconds.
Hold the breath for 4 seconds.
Exhale for 4 seconds.
Hold again for 4 seconds.
Repeat for 5–10 minutes.
Benefits
Boosts lung elasticity.
Enhances oxygen efficiency.
Calms the nervous system.
Caution: If you feel dizzy or lightheaded, stop and resume normal breathing.

Aerobic Exercises (Cardio)
Aerobic exercises are physical activities that raise your heart and breathing rates for an extended period. These include walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, and dancing. As one of the most effective lung health exercises, aerobic activity strengthens both the lungs and heart, improving overall endurance and oxygen efficiency.
When you engage in aerobic exercises regularly, your lungs learn to work harder and more efficiently, increasing lung capacity and improving oxygen delivery to your body’s tissues. Over time, this helps reduce breathlessness and boosts stamina, even during everyday activities.
Including aerobic workouts into your weekly routine is a simple yet powerful way to support respiratory health. These lung health exercises also help manage weight, reduce stress, and improve cardiovascular fitness. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate aerobic activity most days of the week to enjoy long-term lung health benefits.
Examples
Brisk walking
Jogging
Swimming
Cycling
Dancing
How It Helps
Increases oxygen demand, forcing lungs to work harder.
Improves circulation and lung efficiency.
Enhances stamina and endurance.
Duration: Aim for at least 30 minutes, 3–5 times per week.
Bonus Tip: Outdoor cardio also helps you breathe fresher air — just avoid high pollution areas.

Singing and Playing Wind Instruments
Singing, humming, and playing wind instruments are fun yet effective ways to exercise your lungs. These activities require controlled breathing, which engages and strengthens the diaphragm and other respiratory muscles. They are enjoyable lung health exercises that can easily be added to your daily routine.
When you sing or hum, you naturally extend your exhalation, which helps improve lung capacity and breath control. Playing instruments like the flute, trumpet, or harmonica requires steady airflow, promoting stronger lungs and better oxygen exchange. These activities also encourage good posture, which further supports healthy breathing.
Beyond physical benefits, these creative lung health exercises promote relaxation and reduce stress, making them great for emotional well-being too. Whether you’re joining a choir or simply humming around the house, these playful techniques can help keep your lungs strong, especially when practiced consistently over time.
How It Helps
Trains breath control and lung strength.
Improves vocal cord and diaphragm coordination.
Encourages full lung expansion.
Examples
Singing in choirs or karaoke.
Playing instruments like flute, saxophone, trumpet, or harmonica.
Mental Benefit: Singing releases endorphins and reduces stress, which also eases breathing.
Incentive Spirometer Use
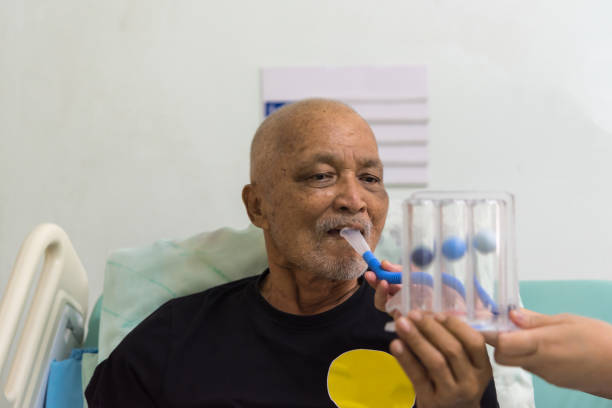
An incentive spirometer is a medical device designed to help lungs recover after surgery, illness, or periods of inactivity. It encourages slow, deep breaths to prevent lung complications like pneumonia and is often recommended as part of post-operative lung health exercises.
Using the device involves inhaling slowly through a mouthpiece, which raises a visual indicator to show how deeply you’re breathing. This process helps expand the lungs, clear mucus, and improve overall breathing efficiency. It’s especially helpful for individuals recovering from respiratory infections or conditions that limit lung function.
Including the incentive spirometer into your daily lung health exercises routine can accelerate recovery and restore lung strength. It’s simple, effective, and often used in hospitals and at home to support respiratory health. Consistent use improves lung capacity and reduces the risk of complications, making it a valuable tool for both prevention and rehabilitation.
How to Use
Sit upright.
Seal your lips around the mouthpiece.
Inhale slowly to raise the marker to the target.
Hold your breath for 3–5 seconds.
Repeat 10–15 times per session, multiple times daily.
Benefits
Prevents pneumonia and lung collapse.
Expands lungs and clears secretions.
Builds inspiratory muscle strength.
Best For: Post-surgery patients or anyone recovering from respiratory illness.
Laughing, Yawning, and Humming
Laughing, yawning, and humming may seem like simple actions, but they are surprisingly effective lung health exercises. These natural behaviors promote deep breathing, clear out stale air, and engage the diaphragm, all of which support stronger lung function.
Laughing causes the lungs to expand fully, enhancing oxygen intake and stimulating the respiratory muscles. Yawning serves a similar purpose by opening the chest and encouraging deep inhalation. Humming creates gentle vibrations that can loosen mucus and improve airflow in the nasal passages and lungs.
Including these lighthearted lung health exercises into your daily routine can improve breathing efficiency and support relaxation. They’re especially helpful for people recovering from illness, feeling stressed, or looking for gentle ways to care for their lungs. Best of all, they’re easy to do anytime, anywhere—and they make lung care feel effortless and enjoyable.
Why They Work
Laughing: Clears out stale air, brings in more oxygen.
Yawning: Triggers a deep breath, stretching your lungs.
Humming: Enhances nitric oxide production which helps keep airways open and reduces inflammation.
Daily Tips
Watch a funny movie.
Sing your favorite song while cooking.
Additional Tips for Optimal Lung Health

💧 Stay Well-Hydrated: Consuming adequate amounts of water each day helps to naturally thin the mucus within your lungs. This makes it easier for your body to clear out environmental irritants, allergens, and other particles, promoting clearer airways and more efficient breathing.
🌫️ Minimize Exposure to Polluted Air: Protect your lungs by limiting time spent in areas with high levels of air pollution, such as near traffic, industrial zones, or areas affected by smoke. At home, consider using high-quality air purifiers and avoid outdoor exercise on days when the air quality is poor.
🧍♂️ Maintain Proper Posture: Poor posture—especially slouching—can compress your chest and restrict full lung expansion. Make a habit of standing tall, sitting upright, and stretching regularly to create more space for your lungs to function at their full potential.
🚭 Avoid Smoking and Secondhand Smoke: Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that damage lung tissue, reduce airway function, and increase the risk of chronic diseases. Quitting smoking—or staying away from secondhand smoke—greatly improves long-term respiratory health.
🏃♀️ Stay Physically Active: Incorporate regular aerobic activities and lung health exercises like brisk walking, swimming, or dancing into your weekly routine. Physical movement encourages deeper breathing, strengthens respiratory muscles, and enhances overall lung capacity.
🌍 Monitor the Air You Breathe: Check the local Air Quality Index (AQI) regularly. When pollution levels are high, reduce outdoor exposure and close windows to prevent harmful particles from entering your living space.
💉 Keep Vaccinations Current: Protect your lungs by staying up to date with recommended vaccines, including the annual flu shot and pneumococcal vaccines. These immunizations help reduce the risk of respiratory infections that can weaken or damage lung tissue.
🩺 Seek Expert Medical Advice When Needed: If you experience persistent coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath, consult a respiratory specialist or pulmonologist. Early diagnosis, combined with appropriate lung health exercises, can help prevent complications and support better breathing long term.
Who Can Benefit from Lung Health Exercises ?
| Who Can Benefit | How Lung Health Exercises Help |
|---|---|
| Healthy Individuals | Help maintain or improve lung capacity and support long-term respiratory efficiency. |
| Athletes | Enhance lung performance, boost endurance, and improve oxygen delivery for peak physical output. |
| Older Adults | Slow the natural decline in lung function and promote independence through better breathing. |
| Individuals with Asthma or COPD | Ease breathing difficulties, reduce symptoms, and improve quality of life with better lung control. |
| Post-COVID or Post-Surgery Patients | Support lung recovery, rebuild respiratory strength, and restore lost function after illness. |
Conclusion
Healthy lungs are essential for a vibrant and active life. In today’s world, where exposure to pollution, allergens, and respiratory illnesses is increasing, protecting and strengthening your lungs is more important than ever. One of the most effective ways to do this is by incorporating lung health exercises into your daily routine.
These exercises include diaphragmatic breathing, aerobic activities, and even enjoyable practices like singing, humming, or laughing. Each technique helps increase lung capacity, improve oxygen flow, and strengthen respiratory muscles. Whether you’re an athlete, recovering from illness, or simply aiming to stay healthy, lung health exercises offer accessible and powerful benefits for all.
Consistency is key. Starting with just five minutes a day can make a noticeable difference over time. As you build the habit, your breathing becomes deeper and more efficient. With regular lung health exercises, you’ll support not only your respiratory system but your overall energy, focus, and well-being.
FAQs
- What are Lung Health Exercises and why are they important ?
Lung Health Exercises are breathing techniques and physical activities that strengthen your lungs, improve oxygen intake, and enhance breathing efficiency. They are important because they help maintain or restore lung function, especially in people exposed to pollution, recovering from illness, or managing conditions like asthma or COPD. - How do Lung Health Exercises benefit people with respiratory conditions ?
For individuals with asthma, COPD, or recovering from respiratory infections, Lung Health Exercises help reduce breathlessness, strengthen respiratory muscles, and clear mucus from the lungs. Regular practice can improve daily functioning and reduce the severity of symptoms over time. - Can healthy people do Lung Health Exercises ?
Yes, even healthy individuals can benefit from Lung Health Exercises. These exercises help maintain strong lung capacity, boost endurance during physical activity, and support better oxygen flow throughout the body, improving overall energy and stamina. - What are some examples of effective Lung Health Exercises ?
Common Lung Health Exercises include diaphragmatic (belly) breathing, pursed-lip breathing, aerobic activities like walking or swimming, and fun practices like singing or playing wind instruments. These exercises increase lung capacity and breathing control when practiced consistently. - How often should I practice Lung Health Exercises ?
It’s best to start with 5–10 minutes of Lung Health Exercises daily and gradually increase the time as you build strength and endurance. Consistency is more important than intensity, and even a few minutes each day can lead to noticeable improvements in lung function.
