Heart disease continues to be one of the top causes of death around the world. However, many of the risks linked to heart problems can be lowered with simple changes in daily habits. Heart disease prevention is possible when individuals make informed choices about their lifestyle, including diet, exercise, and stress management.
Taking steps like eating a balanced diet, staying physically active, and quitting smoking can make a big difference. These actions not only protect the heart but also improve overall health and energy levels. Managing blood pressure, maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, and keeping a healthy weight are also important parts of heart disease prevention.
This article explores the top eight strategies backed by research to help lower the risk of heart disease. Each tip is practical and easy to follow, making it easier to take control of your heart health. By embracing these habits, individuals can enjoy a longer, healthier life while reducing the chances of developing heart disease.

Top Heart Disease Prevention Tips
Quit Smoking and Avoid Tobacco
Smoking is one of the leading risk factors for heart disease. It harms the body by damaging blood vessels, increasing blood pressure, and lowering the amount of oxygen carried in the blood. Even secondhand smoke can raise the chances of developing heart problems. These harmful effects make smoking a serious concern when it comes to heart disease prevention.
The good news is that quitting smoking can bring rapid improvements to heart health. Just one year after quitting, a person’s risk of heart disease drops by 50% compared to someone who continues to smoke. This shows how powerful the decision to quit can be in supporting heart disease prevention efforts.
As more time passes without smoking, the benefits only continue to grow. Long-term nonsmokers have a much lower risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems. By quitting smoking, individuals take a major step toward better health and play a key role in preventing heart disease in the future.
Tips to Quit Smoking:
Seek support from healthcare professionals or smoking cessation programs.

Consider nicotine replacement therapies or medications as prescribed.
Avoid triggers that prompt the urge to smoke.
Engage in stress-relieving activities like exercise or meditation.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity plays a vital role in keeping the heart strong and healthy. It helps improve blood circulation, strengthens the heart muscle, and supports a healthy weight. These benefits are all essential for heart disease prevention, making exercise one of the most effective lifestyle changes for reducing heart risk.
Staying active also helps control blood pressure, manage cholesterol levels, and improve blood sugar regulation. These factors are directly linked to heart health. Whether it’s walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing, even moderate activity done regularly can make a big difference. Small daily efforts add up and contribute to long-term protection against heart disease.
The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week. This can be broken into shorter sessions to fit into busy schedules. Including regular movement in daily life is a simple yet powerful step toward heart disease prevention and better overall health.
At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week (e.g., brisk walking).
Alternatively, 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week (e.g., running).
Incorporate muscle-strengthening activities at least two days per week.
Even small amounts of physical activity can make a difference. If you’re new to exercise, start slowly and gradually increase intensity and duration. Activities like gardening, dancing, or playing sports can also contribute to your weekly exercise goals.
Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet filled with nutrients is an important part of keeping the heart healthy. It helps manage cholesterol levels, control blood pressure, and maintain a healthy weight—all of which are important for heart disease prevention. Choosing the right foods can greatly reduce the risk of heart problems over time.
A heart-healthy diet should include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber that support overall heart function. Reducing intake of salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats also helps lower the risk of high blood pressure and cholesterol.
Making small but consistent changes in eating habits can have a big impact. For example, swapping processed snacks for fresh fruit or choosing grilled foods instead of fried ones can support long-term heart health. By focusing on nutrition, individuals take a powerful step toward heart disease prevention and better overall wellness.

Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a variety of colors to ensure a range of nutrients.
Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains like oats, brown rice, and quinoa over refined grains.
Lean Proteins: Include sources like fish, skinless poultry, legumes, and nuts.
Healthy Fats: Include unsaturated fats from sources like olive oil, avocado, and fatty fish.
Limit Saturated and Trans Fats: Reduce intake of red meat, full-fat dairy, and processed foods.
Reduce Sodium: Limit salt intake to help control blood pressure.
Limit Added Sugars: Avoid sugary beverages and snacks to prevent weight gain and diabetes risk.
Diets such as the Mediterranean and DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diets are particularly beneficial for heart health.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Carrying excess weight, especially around the stomach, raises the risk of heart disease. It puts extra strain on the heart and can lead to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and type 2 diabetes. These conditions are all major risk factors that make heart disease prevention more challenging.
Even losing a small amount of weight can make a big difference. Studies show that losing just 5% to 10% of your body weight can lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of diabetes. These improvements support overall heart health and help reduce the chance of heart problems.
Managing weight through healthy eating and regular physical activity is an important part of heart disease prevention. Simple changes, like eating smaller portions and staying active each day, can have lasting effects. Focusing on gradual, sustainable weight loss can lead to better heart health and a lower risk of future heart-related issues.
Strategies for Weight Management:
Combine a healthy diet with regular physical activity.
Monitor portion sizes and avoid overeating.
Stay hydrated and limit calorie-dense beverages.
Set realistic and achievable weight loss goals.
Monitor and Manage Blood Pressure
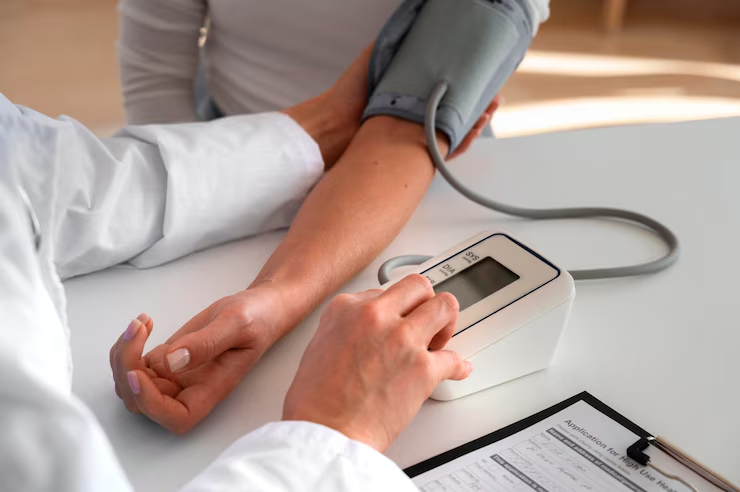
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is one of the main causes of heart disease and stroke. When blood pressure stays high over time, it puts extra stress on the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of serious health problems. Managing blood pressure is a key part of heart disease prevention.
One of the challenges with high blood pressure is that it often has no clear symptoms. Many people may not know they have it until it causes damage. That’s why regular monitoring is so important. Checking your blood pressure at home or during doctor visits can help catch problems early and prevent complications.
The ideal blood pressure target is below 120/80 mm Hg. Reaching and maintaining this level through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and, when necessary, medication can greatly lower the risk of heart disease. Taking steps to control blood pressure is a simple but powerful way to support heart disease prevention and protect overall health.
Tips for Managing Blood Pressure:
Reduce sodium intake and eat a balanced diet.
Engage in regular physical activity.
Limit alcohol consumption.
Manage stress through relaxation techniques.
Follow prescribed medications as directed by healthcare providers.
Control Cholesterol Levels
High levels of LDL cholesterol, often called “bad” cholesterol, can cause plaque to build up in the arteries. This buildup narrows the blood vessels and makes it harder for blood to flow, which increases the risk of heart disease. Keeping LDL levels in check is an important step in heart disease prevention.
On the other hand, HDL cholesterol, known as “good” cholesterol, helps protect the heart. It works by carrying LDL cholesterol away from the bloodstream and back to the liver, where it can be removed from the body. Higher levels of HDL can reduce the risk of blocked arteries and other heart-related issues.
Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels involves eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding tobacco, and sometimes taking medications if recommended by a doctor. These actions all support heart disease prevention by keeping the blood vessels clear and the heart functioning properly. Managing cholesterol is a key part of long-term heart health.
Ways to Improve Cholesterol Levels:
Consume healthy fats from sources like olive oil and fatty fish.
Increase fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Limit intake of trans fats and saturated fats.
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Regular exercise can help raise HDL levels.
Limit Alcohol Consumption

Drinking too much alcohol can negatively affect heart health. It may raise blood pressure, add extra calories that lead to weight gain, and increase the risk of developing heart disease. These effects make excessive drinking a concern when it comes to heart disease prevention.
While some studies suggest small amounts of alcohol might offer limited heart benefits, the risks of overconsumption far outweigh any potential positives. High alcohol intake can also weaken the heart muscle over time, leading to serious conditions like heart failure. That’s why understanding the importance of moderation is essential.
For effective heart disease prevention, it’s best to limit alcohol intake or avoid it altogether. If you choose to drink, the general guideline is no more than one drink per day for women and two for men. Making mindful choices about alcohol helps protect the heart and supports better long-term health. Staying within safe limits plays a vital role in preventing heart problems.
Guidelines for Alcohol Consumption:
Women: Up to one drink per day.
Men: Up to two drinks per day.
One drink is typically defined as:
12 ounces of beer.
5 ounces of wine.
1.5 ounces of distilled spirits.
If you choose to drink, do so in moderation.
Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress can have a serious impact on heart health. It can raise blood pressure, increase heart rate, and place extra strain on the cardiovascular system. Over time, this ongoing stress can raise the risk of heart disease, making stress management a key part of heart disease prevention.
Stress also often leads to unhealthy coping habits. People may turn to comfort eating, smoking, or drinking alcohol to manage their emotions. These behaviors can further increase the risk of heart problems by contributing to high cholesterol, weight gain, and poor lifestyle choices.
To support heart disease prevention, it’s important to find healthy ways to manage stress. Regular exercise, relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation, and spending time with loved ones can all help. Getting enough sleep and setting aside time for enjoyable activities can also reduce stress levels. By staying calm and balanced, individuals can protect their heart and improve their overall well-being.
Effective Stress Management Techniques:
Practice relaxation exercises such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
Engage in regular physical activity to reduce stress hormones.
Maintain a strong social support network.
Set aside time for hobbies and activities you enjoy.
Ensure adequate sleep to help the body recover from stress.
Conclusion

Heart disease prevention is a lifelong commitment that begins with making conscious lifestyle choices. By adopting habits such as eating a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, avoiding tobacco, and managing stress, you significantly reduce your risk of cardiovascular complications. These small, daily decisions build a strong foundation for long-term heart health.
Monitoring your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and weight also plays a critical role in heart disease prevention. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals help catch potential issues early, allowing for timely interventions. Staying informed and proactive empowers you to take control of your heart health.
Ultimately, heart disease prevention is about more than avoiding illness—it’s about improving quality of life and ensuring a healthier, more active future. By making prevention a priority, you not only protect your heart but also invest in a longer, more fulfilling life. It’s never too early or too late to begin taking care of your heart.
FAQs
- What is the most important step in heart disease prevention ?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco is one of the most effective ways to prevent heart disease. - Can heart disease be prevented completely ?
While not all cases can be completely prevented, many risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obesity can be controlled to lower the risk significantly. - How often should I check my blood pressure and cholesterol ?
Adults should have their blood pressure and cholesterol checked at least once every 1–2 years, or more often if they have risk factors or a family history of heart disease. - Does stress really affect heart health ?
Yes, chronic stress can raise blood pressure and lead to unhealthy habits that increase the risk of heart disease. Managing stress is essential for heart disease prevention. - Is moderate alcohol consumption safe for the heart ?
Moderate drinking may be safe for some people, but excessive alcohol use raises heart risks. Limiting intake supports better heart health.
